The food and beverage industry plays a vital role in our economy and society, providing essential goods and services to consumers around the world. However, this industry also generates a significant amount of food waste, which has significant economic, environmental, and social impacts. Food waste and food recovery are critical issues that need to be addressed by the food and beverage industry to ensure sustainable production and consumption.
Food Waste and Food Recovery
Food waste refers to any food that is discarded or lost along the supply chain from production to consumption. This can include food that is damaged or spoiled during production, food that is not sold by retailers or restaurants, and food that is thrown away by consumers. Food waste is a significant problem for the food and beverage industry, with estimates suggesting that around one-third of all food produced globally is lost or wasted each year.

There are several reasons why food waste is such a significant issue. Firstly, food waste is a significant economic loss for the food and beverage industry. When food is wasted, it represents lost revenue for producers, retailers, and restaurants, and it also increases the costs of food production, storage, and transportation. Secondly, food waste has significant environmental impacts, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land use. When food is wasted, it also represents a waste of the resources used to produce it, including water, energy, and land. Finally, food waste has significant social impacts, contributing to food insecurity and hunger, particularly in developing countries.
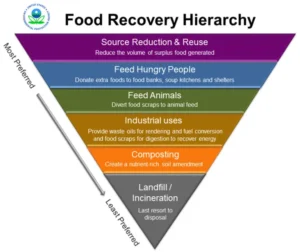
To address the issue of food waste, many organizations in the food and beverage industry have started to implement food recovery programs. Food recovery refers to the collection and redistribution of surplus food to those in need, rather than allowing it to go to waste. Food recovery programs can take many forms, including food donation, food recycling, and composting. By recovering surplus food, these programs help to reduce food waste and provide much-needed food to those who need it most.
There are several benefits to implementing food recovery programs in the food and beverage industry. Firstly, food recovery programs can help to reduce the economic costs of food waste by redirecting surplus food to those in need. This can help to reduce the financial losses associated with food waste and also provide a significant economic benefit to those who receive the donated food.
Secondly, food recovery programs can have significant environmental benefits, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental impacts associated with food waste. Finally, food recovery programs can have significant social benefits, providing much-needed food to those who are food insecure or experiencing hunger.
There are several ways in which food recovery programs can be implemented in the food and beverage industry. One approach is through food donation programs, where surplus food is donated to charities, food banks, or other organizations that distribute food to those in need. Many large food retailers and restaurants have established food donation programs, partnering with local charities and food banks to ensure that surplus food is redirected to those who need it most.
Another approach is through food recycling programs, where food waste is recycled into other products, such as animal feed or fertilizer. This approach can help to reduce the environmental impacts of food waste, but it does not address the issue of food insecurity or hunger.
Composting is another approach to food recovery, which involves the decomposition of food waste into compost, which can be used as a soil amendment. Composting can help to reduce the environmental impacts of food waste, as well as providing a valuable resource for agriculture. However, composting does not provide a solution to food insecurity or hunger, and it may not be feasible in all locations.
There are several challenges to implementing food recovery programs in the food and beverage industry. Firstly, there is often a lack of infrastructure and resources to support food recovery programs, particularly in developing countries. Food donation programs, in particular, require significant coordination and logistics to ensure that surplus food is distributed effectively and safely.
Secondly, there are legal and regulatory barriers that may prevent food recovery programs from operating effectively. For example, in some countries, there are liability concerns associated with donating food, which can make it difficult for retailers and restaurants to participate in food donation programs. Additionally, there may be health and safety regulations that restrict the donation of certain types of food, which can limit the effectiveness of food recovery programs.
Finally, there is often a lack of awareness and education about the importance of food recovery among consumers, retailers, and restaurants. Many people are unaware of the scale of food waste and the benefits of food recovery programs, which can make it difficult to generate support and participation in these initiatives. Increasing public awareness and education about food waste and food recovery can help to create a culture of sustainability and reduce the amount of food that is wasted.
In conclusion, food waste and food recovery are critical issues that need to be addressed by the food and beverage industry to ensure sustainable production and consumption. Food waste represents a significant economic, environmental, and social problem, with significant impacts on the industry and society.
Implementing food recovery programs, such as food donation, food recycling, and composting, can help to reduce the economic, environmental, and social impacts of food waste, while also providing much-needed food to those who are food insecure or experiencing hunger.
However, there are several challenges to implementing food recovery programs, including a lack of infrastructure, legal and regulatory barriers, and a lack of awareness and education. Overcoming these challenges will require collaboration and cooperation across the food and beverage industry, as well as increased public awareness and education about the importance of food waste and food recovery.